Introduction
In this workshop, we will build a comprehensive solution to manage the lifecycle and security of your container images by leveraging the power of Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) along with related AWS services. You will be guided through a DevSecOps process, from initial setup to automation, security, and monitoring.
Architecture Overview
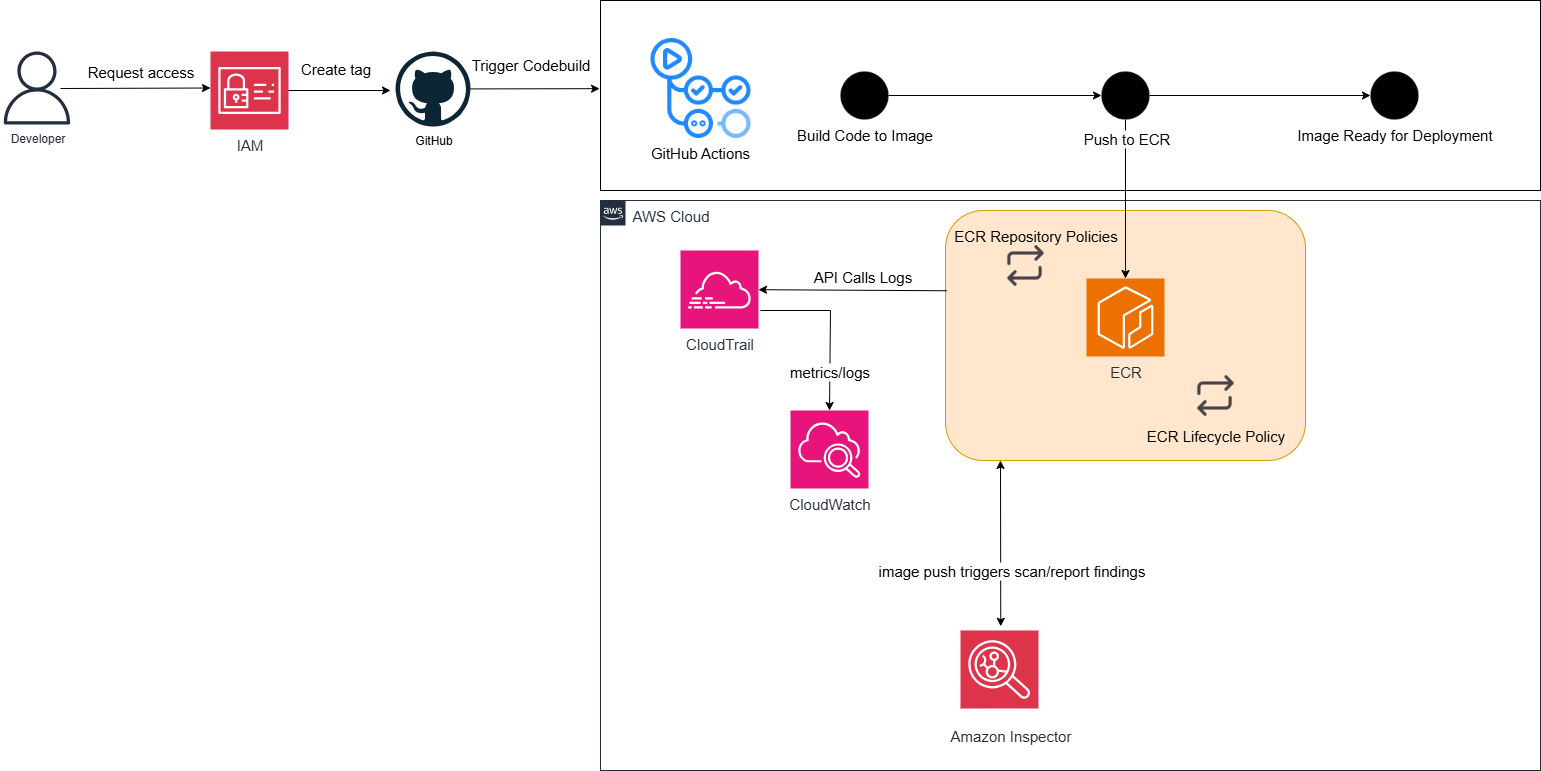
The architecture above illustrates the main workflow in this workshop:
Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD):
- Developers begin by requesting access through IAM (Identity and Access Management).
- Code changes are managed in GitHub. When a new tag is created or code is pushed, GitHub Actions will be triggered.
- GitHub Actions serves as our primary CI/CD tool. It will perform the steps: “Build Code to Image” (building a Docker image from the source code) and then “Push to ECR” (pushing the built image to Amazon Elastic Container Registry).
- Once successfully pushed, the image will be “Image Ready for Deployment” (ready for deployment).
Registry Management and Security in AWS Cloud:
- Amazon ECR is the central repository for your container images. Here, ECR Repository Policies will manage detailed access rules, and ECR Lifecycle Policy will automatically manage the lifecycle of images, helping to clean up old or unnecessary versions.
- When a new image is pushed to ECR, this action will “image push triggers scan/report findings” by Amazon Inspector. Amazon Inspector will automatically scan the image to detect known security vulnerabilities.
Monitoring:
- AWS CloudTrail automatically records “API Calls Logs” from ECR and other AWS services. These logs are sent to Amazon CloudWatch for storage and “metrics/logs” analysis. CloudWatch also plays a role in overall monitoring and can trigger alarms based on metrics.
- Amazon Inspector identifies security vulnerabilities in container images you store in Amazon ECR.
Resource Cleanup: Finally, the workshop will also guide you on how to clean up all created AWS resources to avoid unwanted costs.
This workshop will provide you with practical knowledge and essential skills to build a modern, secure, and cost-effective container image management workflow in the AWS environment.
Key AWS Services Used
In this workshop, we will interact with and configure several important AWS services to build a comprehensive container image management system. Below is a basic introduction to each service:
Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
Amazon ECR is a fully managed, secure, scalable, and reliable Docker container registry service. ECR allows developers to easily store, manage, share, and deploy their Docker images. It integrates tightly with Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS), Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), and AWS Lambda, as well as AWS and third-party CI/CD tools.
With Amazon ECR, you don’t need to operate your own container registry infrastructure or worry about its scaling, security, and availability. ECR provides:
- High Security: Images are encrypted at rest and in transit. IAM integration for fine-grained access control.
- Scalability: Automatically scales to meet your image storage needs.
- High Performance: Fast image retrieval for your container deployments.
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service that helps you securely control access to your AWS resources. With IAM, you can manage who is authenticated (signed in) and authorized (has permissions) to use resources. In this workshop, IAM serves as the foundation for security by:
- Managing Users: Creating and managing AWS users for console or CLI access.
- Managing Roles: Allowing AWS services or third parties (like GitHub Actions) to assume a role with temporary permissions to perform tasks.
- Managing Policies: Defining specific permissions (allow or deny) that users or roles can perform on your AWS resources, ensuring the principle of “least privilege.”
GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) platform built directly into GitHub. It allows you to automate your software development workflows directly from your GitHub repository. In this workshop, GitHub Actions is used to:
- Automate Build: Automatically build Docker images upon code changes.
- Automate Push: Push the built Docker images to ECR.
- Integrate: Securely connect with AWS via IAM Roles and OpenID Connect to perform actions on ECR.
Amazon Inspector
Amazon Inspector is an automated vulnerability management service that helps you discover and continuously scan AWS workloads for vulnerabilities. When integrated with ECR, Amazon Inspector can:
- Automated Image Scanning: Automatically scan new container images as they are pushed to ECR.
- Vulnerability Detection: Identify known security vulnerabilities (CVE - Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) in the operating system, application packages, and dependencies of the images.
- Detailed Reporting: Provide detailed information on vulnerabilities found, their severity, and remediation guidance.
AWS CloudTrail
AWS CloudTrail is a service that enables you to monitor and record user activity and API calls across your AWS services. It provides a history of events in your AWS account. CloudTrail is crucial for:
- Security Auditing: Providing a detailed audit trail of all interactions with ECR and other services, helping to track who did what, when, and where.
- Compliance Analysis: Supporting compliance requirements by providing evidence of account activity.
- Troubleshooting: Helping diagnose and troubleshoot issues by reviewing the sequence of events that occurred.
Amazon CloudWatch
Amazon CloudWatch is a monitoring and management service that allows you to collect and access metrics, logs, and events from your AWS applications, resources, and services. In the workshop, CloudWatch is used to:
- Collect Metrics: Automatically collect performance and operational metrics from ECR (e.g., repository size, image push/pull counts).
- Monitor Logs: Store and analyze logs from other services (e.g., API logs from CloudTrail).
- Create Alarms: Set up alarms based on metric thresholds or patterns in logs to proactively notify about potential issues.